10 Best Uses of Levulinic Acid for Sustainable Applications
Levulinic Acid has emerged as a key player in the realm of sustainable applications, garnering attention from researchers and industry experts alike. Renowned chemical engineer Dr. Emily Turner once stated, “Levulinic Acid is not just a platform chemical; it represents a transformative approach to sustainability, offering opportunities across various sectors.” This statement encapsulates the growing recognition of Levulinic Acid as an essential building block for eco-friendly bioproducts.
As the world shifts towards greener alternatives, Levulinic Acid is leading the charge in developing sustainable solutions. Derived from the biomass of agricultural residues, this versatile compound can be utilized in numerous applications, ranging from biofuels to pharmaceuticals. The potential of Levulinic Acid lies in its ability to serve as a precursor for a variety of valuable chemicals, thereby promoting a circular economy and minimizing waste.
In this exploration of the ten best uses of Levulinic Acid, we will delve into its multifaceted applications that not only drive innovation but also align with sustainable practices. By highlighting its significance, we aim to underscore the vital role Levulinic Acid plays in shaping a more sustainable future for various industries.

Overview of Levulinic Acid and Its Sustainable Importance
Levulinic acid, a versatile platform chemical derived from biomass, is garnering attention for its sustainable applications in various industries. Its ability to serve as a precursor for biofuels, biodegradable plastics, and other high-value chemicals makes it a crucial component in the shift toward a more sustainable economy. With increasing concerns about fossil fuel dependency and environmental degradation, the sustainable importance of levulinic acid cannot be overstated. It represents a viable alternative to petroleum-based products, contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and promoting circular economy practices.
**Tip:** When exploring sustainable materials, consider the sourcing of biomass for levulinic acid production. Opt for waste materials or byproducts from agriculture to maximize sustainability benefits and minimize environmental impact.
Additionally, levulinic acid can be utilized in the agricultural sector as a natural pesticide and herbicide. Its capacity to enhance soil health and improve crop yields aligns with eco-friendly farming practices. This biobased chemical serves as an excellent example of how innovation can lead to greener agricultural solutions, helping farmers reduce reliance on synthetic chemicals while maintaining productivity.
**Tip:** Farmers looking to implement sustainable practices should investigate local regulations regarding biopesticides and find training opportunities to better understand the application of levulinic acid in pest management.
10 Best Uses of Levulinic Acid for Sustainable Applications
Key Properties of Levulinic Acid for Environmental Applications
Levulinic acid, a versatile and renewable platform chemical derived from biomass, exhibits a range of key properties that make it particularly valuable for sustainable applications. One of its most significant characteristics is its ability to serve as a biodegradable solvent. This property allows levulinic acid to replace more toxic and environmentally harmful solvents in various industrial processes. Additionally, its low volatility contributes to reduced air pollution and enhanced safety during handling, which is crucial in promoting a safer working environment.
Another important property of levulinic acid is its role as a potential building block for biofuels and bioplastics. Its chemical structure allows for various transformation reactions, which can result in the production of eco-friendly alternatives to fossil fuels and conventional plastics. Given the growing concern over climate change and pollution, leveraging levulinic acid for these applications aligns perfectly with the global push towards greener technologies. Moreover, its compatibility with existing chemical processes enables a smoother transition to more sustainable practices in various industries, highlighting its importance in a future focused on environmental sustainability.
Top 10 Innovative Uses of Levulinic Acid in Green Chemistry
Levulinic acid, a versatile platform chemical derived from biomass, has emerged as a key player in green chemistry, showcasing innovative applications that align with sustainability goals. One of its most notable uses is as a precursor for biofuels. Research indicates that levulinic acid can be efficiently converted into high-value biofuels such as butanol, demonstrating a potential to reduce dependency on fossil fuels. According to a report from the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the biofuel industry is projected to grow significantly, and incorporating levulinic acid could enhance the overall carbon efficiency of this market.
In addition to energy applications, levulinic acid serves an essential role in the production of biodegradable plastics. Current research published in the Journal of Polymers suggests that levulinic acid-derived polymers can compete with conventional petrochemical-based plastics, providing similar mechanical properties while offering a greener alternative. As the global shift towards circular economies intensifies, these biopolymer materials are expected to gain traction. A recent market analysis from Grand View Research indicates that the bioplastics market is set to reach USD 44.93 billion by 2028, highlighting the increasing demand for sustainable materials. Levulinic acid stands at the forefront of this trend, combining ecological responsibility with innovation.
Levulinic Acid in Biofuels: A Sustainable Energy Source

Levulinic acid, a versatile platform chemical derived from the hydrolysis of cellulose, has garnered attention in the renewable energy sector for its potential role in biofuel production. As a bio-based compound, it holds promise as an alternative to fossil fuels, contributing to greener energy solutions. According to a report from the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), sustainable biofuels could provide up to 30% of global energy needs by 2050, with levulinic acid serving as a key intermediate for various biofuels, including diesel and jet fuel substitutes.
One of the most significant advantages of levulinic acid is its ability to be converted into high-energy-density fuels such as levulinate esters. These esters exhibit comparable properties to conventional fuels, making them ideal candidates for blending with existing fuel supplies. The potential economic benefit is substantial; the global biofuel market is expected to reach over USD 200 billion by 2025, driven by rising environmental concerns and regulatory incentives for cleaner energy sources.
Tips: When exploring biofuel options, consider incorporating levulinic acid-derived fuels into your energy mix to reduce carbon emissions. Additionally, keeping an eye on technological advancements in extraction and conversion processes can yield efficient production methods that further boost sustainability. Engaging in education on renewable energy can help you make informed decisions about adopting biofuels in your community.
Future Directions and Potential of Levulinic Acid in Sustainable Practices
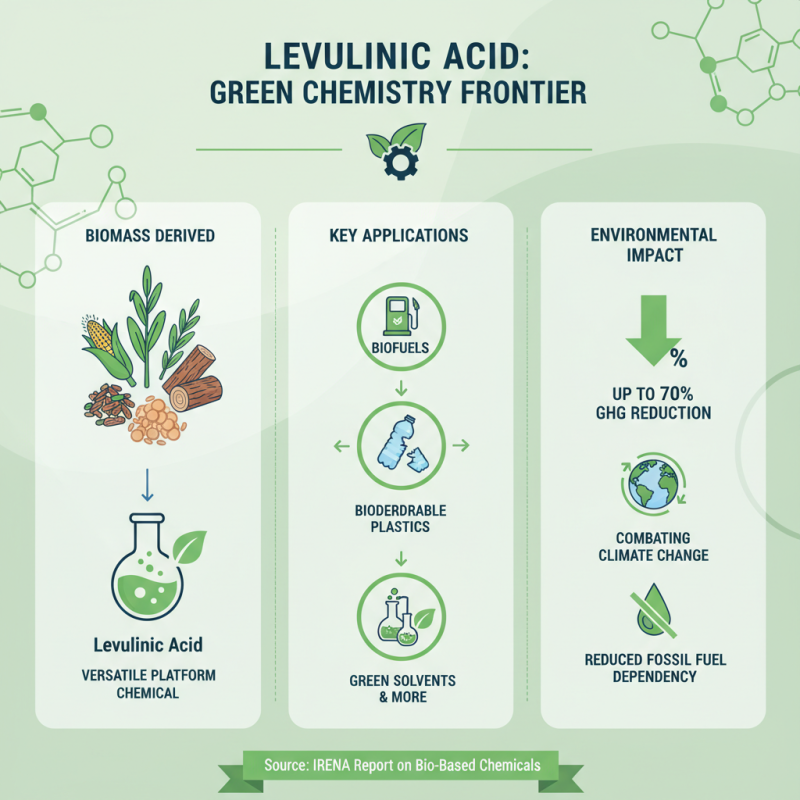
Levulinic acid, a versatile platform chemical derived from biomass, has garnered significant attention for its potential in sustainable practices. Its applications range from biofuels to biodegradable plastics, positioning it at the forefront of green chemistry advancements. According to a report by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the adoption of bio-based chemicals such as levulinic acid could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 70% compared to conventional petrochemical processes. This aligns well with the growing global movement towards sustainability and the reduction of fossil fuel dependency.
Future directions in the utilization of levulinic acid look promising, particularly in the field of renewable energy and bioplastics. Research indicates that leveraging levulinic acid in the production of second-generation biofuels can significantly enhance fuel properties while also lowering production costs. According to a 2022 study published in the Journal of Cleaner Production, integrating levulinic acid into biorefinery processes could lead to more efficient resource use and waste reduction, with the potential to improve overall economic viability. As policies favoring sustainable materials and renewable energy sources continue to evolve, the role of levulinic acid will likely expand, enabling innovative approaches to tackle environmental challenges.
Related Posts
-

Elevating Global Standards with Exceptional Quality Best Levulinic Acid from China
-

Unlocking the Potential of Best Levulinic Acid Technical Parameters and Application Guide
-

How to Maximize the Benefits of Levulinic Acid in Biochemical Applications
-

5 Proven Tips to Source High-Quality Levulinic Acid for Your Business Needs
-

Revolutionizing Nutrition: Industry Applications of Best Vitamin C Coated Supplements and Their Efficacy
-

Top 7 Tips for Selecting the Best Agmatine Sulfate Manufacturer in the Industry